Carbon Foam Composite Tooling
CFOAM® – BASED CARBON FOAM COMPOSITE TOOLING OFFERS AN ALTERNATIVE TO CONVENTIONAL INVAR®, STEEL, AND ALUMINUM TOOLS – SIMPLIFYING TOOL DESIGN AND REDUCING THE TIME TO BUILD A TOOL.
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW
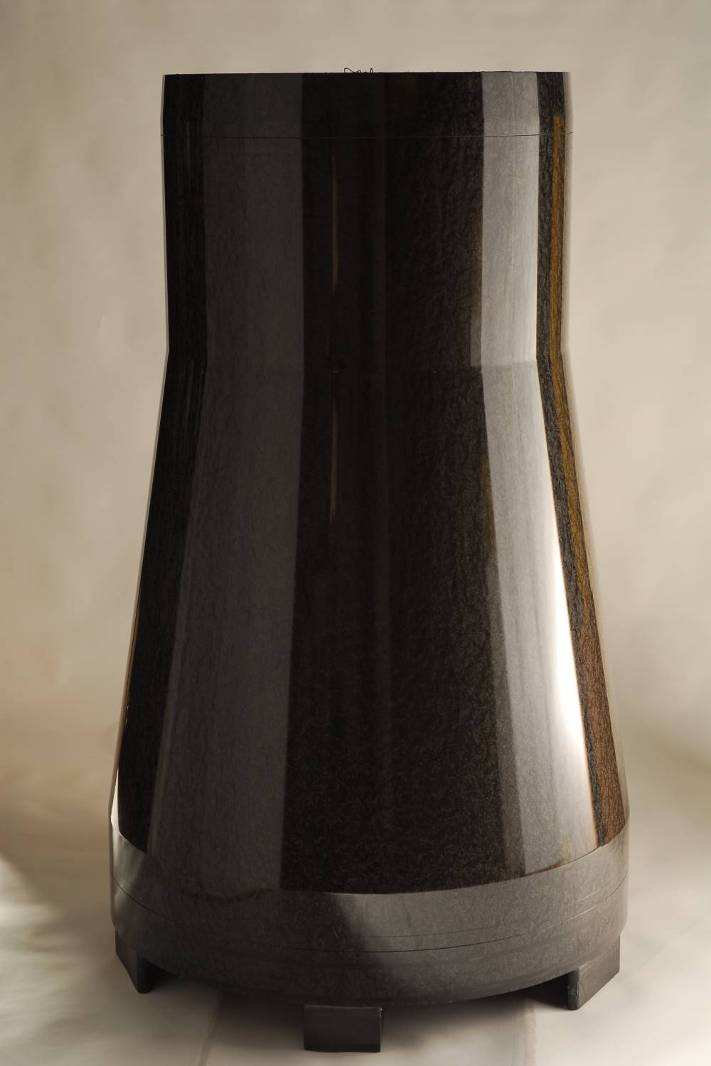

Construction of aircraft, spacecraft, missile parts, automobiles, and sporting goods equipment is rapidly moving to carbon fiber-reinforced thermoset and thermoplastic resins, resulting in higher strength-to-weight ratio, higher stiffness, and less susceptibility to corrosion and fatigue.
CFOAM® -based carbon foam composite tooling offers an alternative to conventional Invar®, steel, and aluminum tools – simplifying tool design and reducing the time to build a tool.
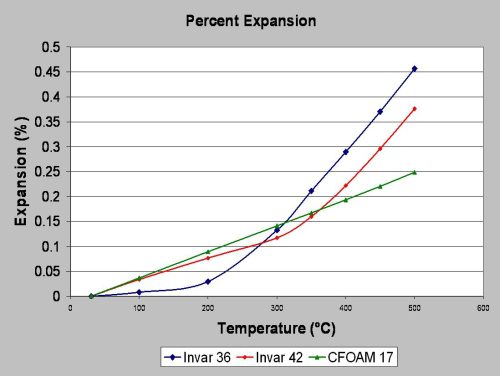
Tooling must be low cost, rigid, durable, thermally stable – offer a low CTE (coefficient of thermal expansion), and in many cases, be lightweight.
For dimensional stability of the tool, the CTE must closely match the part being produced. CFOAM® carbon foam has a very uniform thermal expansion when compared with Invar® 36 and 42. This enables post curing of the composite parts on the tool with high temperature BMI resins.
CFOAM LLC performed a comprehensive benefit analysis comparing the use of CFOAM® carbon foam versus Invar®, aluminum, and steel tools.
The finding identified that the use of CFOAM® carbon foam would not just be a suitable alternative to the current method, but also provide the following advantages:
- Low coeffecient of thermal expansion for composite tooling more closely matching composite part
- Lower fabrication costs
- Lighter weight tools
- Tooling easier to modify or repair
- Improved performance durability
- Increased autoclave part throughput due to low mass tooling
 Touchstone has developed unique process methods critical for manufacturing carbon foam composite tooling. Both rapid and durable tooling methods have been developed.
Touchstone has developed unique process methods critical for manufacturing carbon foam composite tooling. Both rapid and durable tooling methods have been developed.
Tool performance was tested and evaluated. Important developments were made in tooling surface coatings, including continuous and chopped fiber with BMI resins. CFOAM® carbon foam composite tools are currently in-service today and are successfully being used at commercial composite lay-up production facilities.
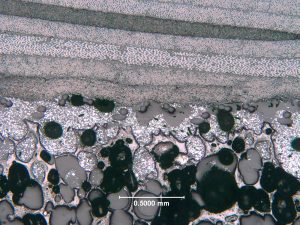
Optical Microscopy of Tooling
Surface Cross-section
COMPOSITE TOOLING FABRICATION WITH CFOAM® CARBON FOAM
Block Bonding
 Dimensions for the tool will be necessary before any work can begin. When the size and shape are determined, CFOAM® carbon foam blocks are then stacked to the desired finished part geometry.
Dimensions for the tool will be necessary before any work can begin. When the size and shape are determined, CFOAM® carbon foam blocks are then stacked to the desired finished part geometry.
Use the CFOAM® carbon foam bonding adhesive to adhere all of the blocks together in the proper form. Use a notched trowel to ensure a sufficient amount of adhesive has been applied. Apply the adhesive to both the surface and the edges where any of the blocks are touching each other and follow the adhesive curing instructions.
Rough Machining
 After the adhesive has dried, the resulting CFOAM® carbon foam block can be machined into the proper shape. However, this machined product should be undersized from the actual dimensions to allow room for the composite surfacing material.
After the adhesive has dried, the resulting CFOAM® carbon foam block can be machined into the proper shape. However, this machined product should be undersized from the actual dimensions to allow room for the composite surfacing material.
The specific under-cut will vary depending upon the type of surface being applied. Several different surfacing materials have been developed and tested.
Consult CFOAM LLC technical support for additional information regarding specific surfacing material.
Adding Composite
 The unfinished tool is now ready for the application of the adhesive and surfacing materials to the outside surface of the rough machined CFOAM® carbon foam. Apply adhesive film cut-to-size to the bottom of the tool. In this example, a bi-directional carbon pre-preg is used. The weight of this film varies and should be adjusted as needed. The amount of material will primarily be driven by the durability and handling requirements of the tool. The pre-preg is now applied to the bottom of the tool after being cut to size slightly larger than the actual measurements to allow for trimming. Each individual piece is trimmed before the next layer is applied.
The unfinished tool is now ready for the application of the adhesive and surfacing materials to the outside surface of the rough machined CFOAM® carbon foam. Apply adhesive film cut-to-size to the bottom of the tool. In this example, a bi-directional carbon pre-preg is used. The weight of this film varies and should be adjusted as needed. The amount of material will primarily be driven by the durability and handling requirements of the tool. The pre-preg is now applied to the bottom of the tool after being cut to size slightly larger than the actual measurements to allow for trimming. Each individual piece is trimmed before the next layer is applied.
 Once all the pieces are applied to the bottom, begin working on the sides of the tool. Apply the adhesive film as before and follow the same process until all sides are covered. Flip the tool over and apply the adhesive to the top surface. This process can be done in sections if the tool has a complex geometry to ensure that it adheres properly. Press onto the tool firmly to avoid air pockets behind the adhesive. Apply the surface material in sections per the engineering ply layout.
Once all the pieces are applied to the bottom, begin working on the sides of the tool. Apply the adhesive film as before and follow the same process until all sides are covered. Flip the tool over and apply the adhesive to the top surface. This process can be done in sections if the tool has a complex geometry to ensure that it adheres properly. Press onto the tool firmly to avoid air pockets behind the adhesive. Apply the surface material in sections per the engineering ply layout.
Final Preparation and Processing
Place the tool into a vacuum bag and autoclave cure it. Vacuum bagging materials and procedures are dependent upon specific resin systems and may be varied depending upon part geometries.
Remove the composite tool from the autoclave and the vacuum bag. Machine it to final size. When the composite tool is completed in the mill, a seal coating is applied to the top surface and will fill any pinholes or scratches on the surface. Finally, wet sand the tool for a polished finish. The surface hardness on this kind of tool has been measured at 83 Rockwell B, which is comparable to many Invar® tool surfaces.


HOW TO GET STARTED WITH COMPOSITE TOOLING – CFOAM LLC CAN PROVIDE:

CFOAM® carbon foam billets

Bonded CFOAM® carbon foam blocks laid up to specified dimensions

Custom machined CFOAM® carbon foam parts
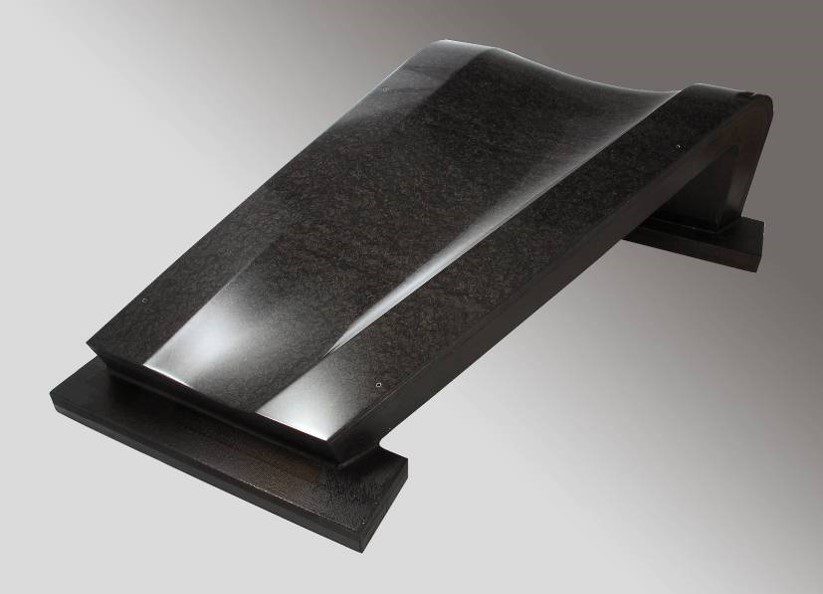

A complete composite tool
Whatever your needs for lightweight aerospace composite tooling or other tooling applications, call or email us at:
Email: info@cfoam.com


